|
Centrosome - an organelle which gives the cell it’s shape and helps the cell reproduce. (the cell uses this skeleton to move around)
|
Cell Membrane- The thin film like outer layer that holds the cell together. It works like a gatekeeper allowing certain substances in and out.
|
ATP Adenosine Triphosphate - store the cells energy (like the cells money)
|
Cell Wall - Cell walls are in plant cells and are made of specialized sugars called cellulose. Cell walls also help a plant keep its shape and protect the cell. They also help plants grown to great heights. |
|
Cytoplasm - is the fluid that fills a cell which can turn 1 glucose into 2 ATP. The cells organelles are suspended in the cytoplasm.
|
Glucose- is like fuel - the cell uses it and turns it into ATP. This is the scientific word for sugar.
|
Mitochondria - like the cells power plant. The mitochondria powers the cell from the food we eat.
Makes 1 glucose into 38 ATP

|
Vacuole - These are storage bubbles found in cells. They are found in both plants and animal cells, but are much larger in plant cells. Vacuoles can store a variety of nutrients a cell might need to survive.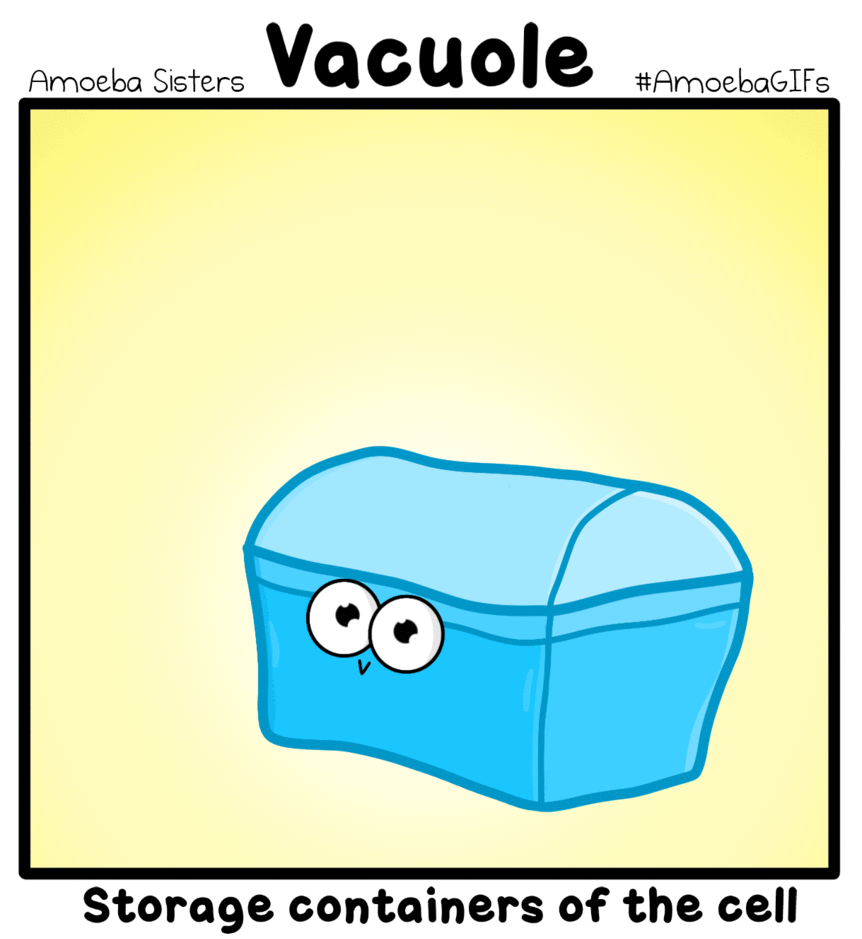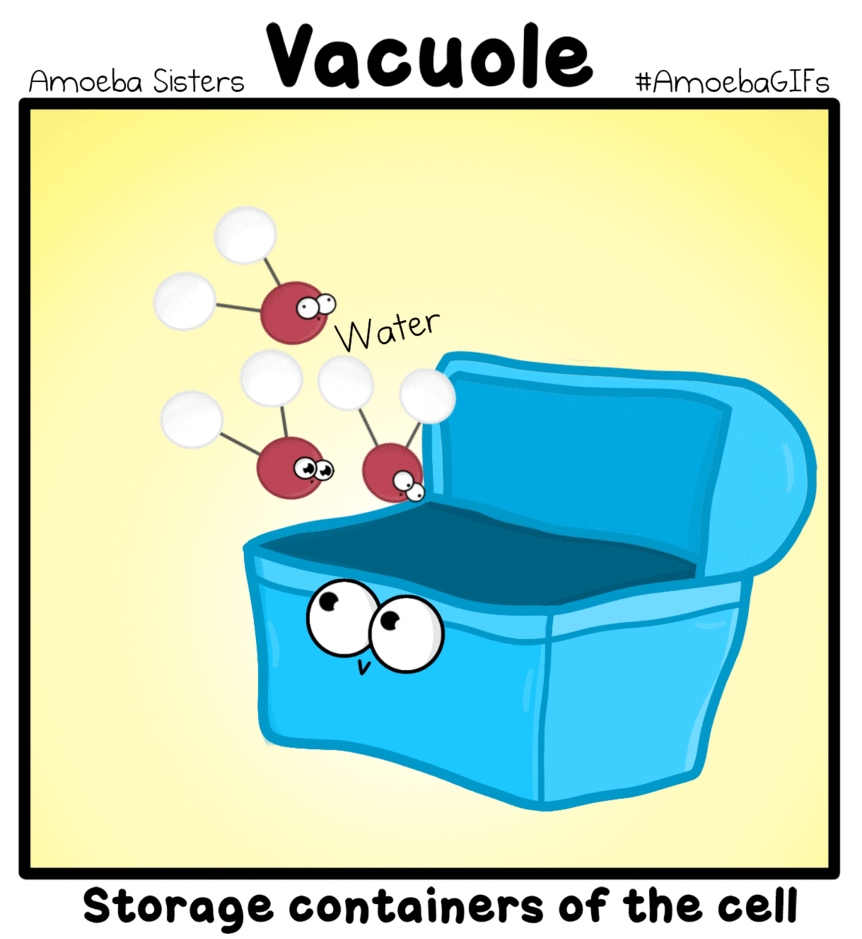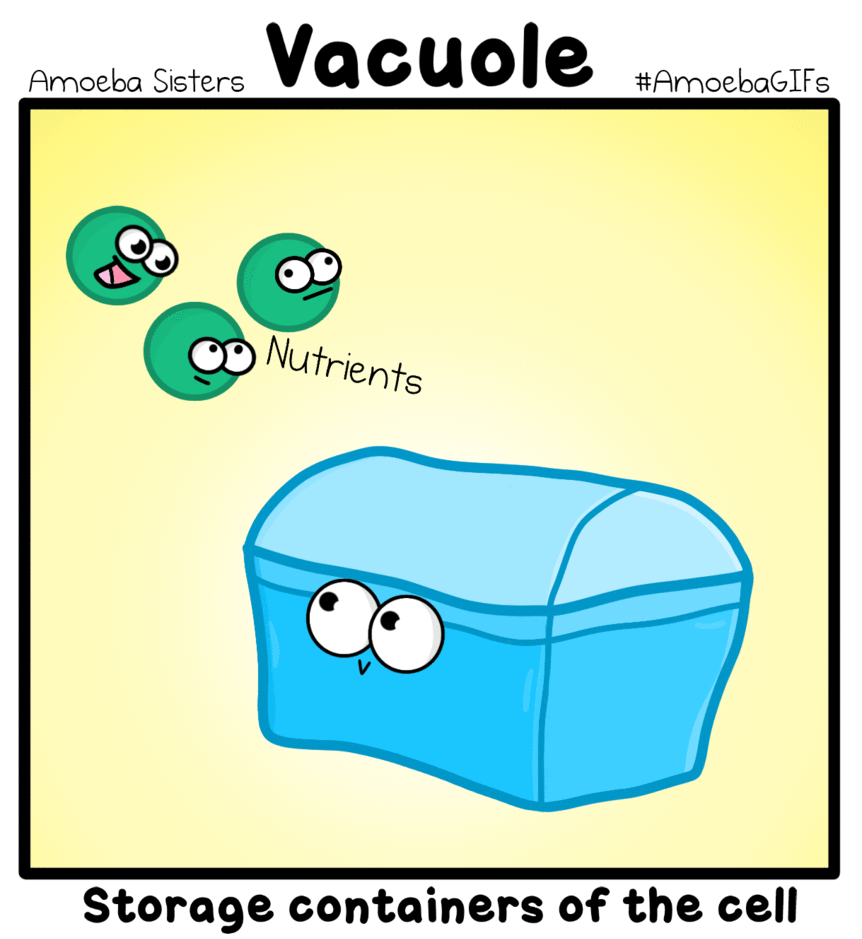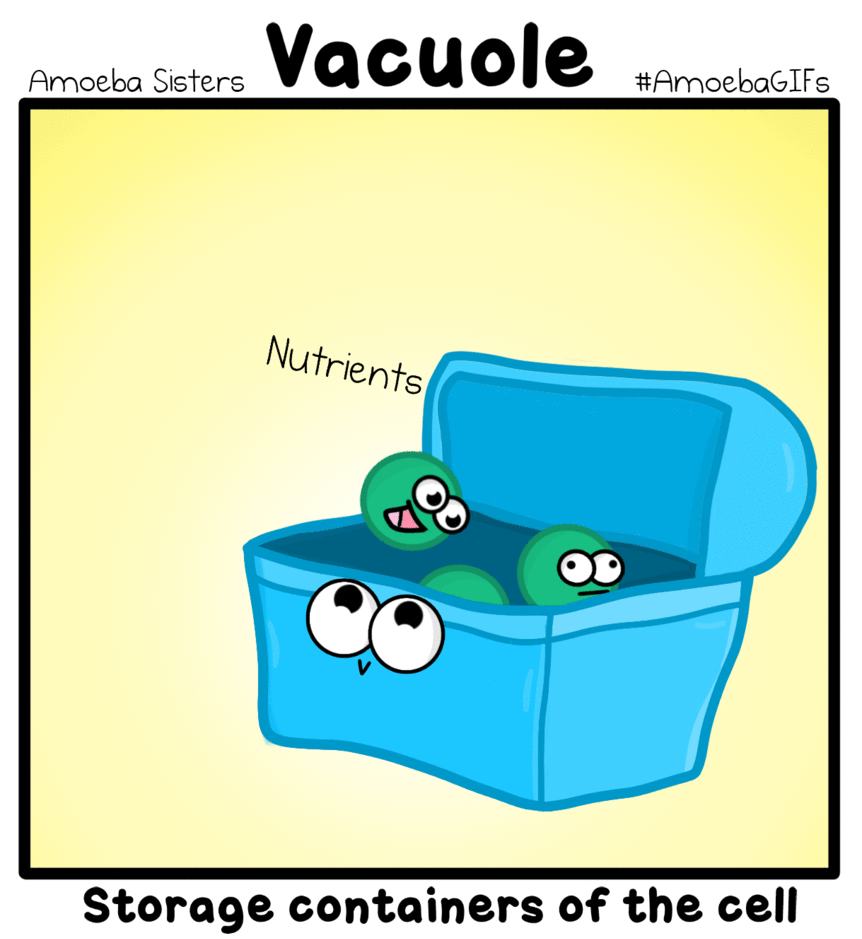 |
|
Organelle- Cellular organs. Each organelle has a special job and is suspended in the cytoplasm.
|
Nucleus - the central command structure of the cell which directs all the activities. The nucleus contains the cell’s DNA. 
|
Nucleic Acid - makes RNA, which is like a blueprint or map for protein.
|
Chloroplast - an organelle found in plant cells which use sunlight to make glucose. Plants are green because they have chloroplasts. |
|
Amino Acids - are molecules that make protein. They are the cells building blocks.
|
Ribosomes - are like the factories, the nucleus gives them orders and they make things using the nucleic acids
|
Slicer Enzymes - tracks down and kills viral RNA.
|
Defensins - are proteins in the cell membrane which block viruses from entering |
|
Viruses - invade the cell and reproduce. A virus has a protein coat and viral RNA. Viruses try to get their RNA to the ribosomes. Then the ribosomes make more viruses.
|
Fatty Acids - the cytoplasm can turn 4 glucose into 1 fatty acid, which happens when your cell has too much glucose. Fatty acids are molecules used to make the membrane
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum (E.R) - is an organelle where the membrane is produced. It produces vesicles

|
Peroxisome - is a vesicle made by the E.R. which absorbs free radicals. |
|
Free Radicals - poisonous garbage which mitochondria produce along with ATP. The free radicals can damage organelles.
|
DNA Repair Enzymes - are special proteins which repair the nucleus.
|
Vesicles - is a membrane bubble with protein inside, there are many types of vesicles. vesicles also carry organelles.
|
Golgi Body - is an organelle which sorts and processes vesicles. |
|
Lysosome - is a vesicle filled with acid and can recycle large organelles.
|
Cell Theory - The ideas that
1.All living things are made of cells.
2.Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things.
3.Living cells come only from other living cells.
|
|
|
Comments (0)
You don't have permission to comment on this page.